We offer two series of LED mini bulbs: Smart Series and Eco Series. Please find how to choose between the two series below:
| PRODUCT SERIES | SMART SERIES | ECO SERIES |
| HYPER FLASH PREVENTION | RECOMMENDED for use in turn signals and any other application with CANBus related errors. SMART series would not require a load resistor to fix hyper flashes. | NOT recommended to use in turn signals and any other application with CANBus related errors. A load resistor would be required to fix hyper flashes. |
| BEST PERFORMANCE | RECOMMENDED if you want to upgrade your tail light or signal light to LEDs. | RECOMMENDED for best for sider markets, back-up lights and license plate light upgrade. |
| BEST VALUE FOR MONEY | RECOMMENDED for easy install (no load resistor required) of front or rear turn signal light upgrade to LEDs. | RECOMMENDED for the best value for money |

The bulb replacement procedure will also be found in your user manual.


#3: Search your vehicle in Year/Make/Model search engine. Use the vehicle search engine on our website. Search by Year, Make, Model or sub model and Qualifier (type of headlamp/fog lamp) your vehicle came with.

Click Search button then select the bulb type on the sidebar on the left. The search result will show you the LED bulb available.

In some vehicles, you may not able to access the light bulbs very easily. In some newer vehicles, you may also need to remove the front bumper cover or even remove the whole headlamp assembly in order to access and change the bulbs.
The Car Care Kiosk Website is a good resource to find videos of how to access and change any vehicle bulb.
STEP 1: Go to the link https://www.carcarekiosk.com/.
STEP 2: Search your vehicle by Make / Model / Year / Engine.

STEP 3: Select the bulb type you are looking to change.

STEP 4: The video will guide you step by step to access and change your light bulbs.

Keywords: change vehicle bulb, access light bulbs, Car Care Kiosk, remove bumper cover, headlamp assembly, vehicle maintenance, bulb replacement guide.
We have two product options for headlight and fog light LED conversion. Please see the guidelines below on how to choose between the CONCEPT and XTREME series:
| PRODUCT SERIES | CONCEPT SERIES | XTREME SERIES |
| DRIVING IN CITY: | RECOMMENDED for everyday city driving with greatly improved style and visibility. Focused beam and precise cut off line create a legal driving beam with zero glare. | NOT recommended to use in your low beam headlight if you are driving mostly in the city. |
| DRIVING RURAL/OFF-ROAD: | Compatible with projector headlamp. Improved brightness than the stock bulb but not as much as HID’s. | RECOMMENDED for its extreme brightness and light range that exceed a 35W HID system |
| LOW BEAM HEADLIGHT: | RECOMMENDED for low beam headlights with focused beam pattern and precise cut off line with zero glare. | Only recommended for low beam headlights if you are driving mostly in rural and off road conditions due to extreme brightness. |
| HIGH BEAM HEADLIGHT: | RECOMMENDED for high beam headlights for focused beam pattern | RECOMMENDED for high beam headlights with supreme brightness and light range |
| PROJECTOR LAMP: | Compatible with projector headlamp. Improved brightness than the stock bulb, but not as much as HID’s. | RECOMMENDED for projector headlamps for brightness equal to 35W HID’s. |
| FOG LIGHTS | RECOMMENDED for perfect fog beam pattern and reliability in inclement weather conditions. | NOT recommended to install in fog lights without dust caps or rubber boots. Excessive elements would affect the life of the fan cooling system. |
| EXTREME TIGHT SPACES | RECOMMENDED for any tight spaces. This bulb is designed to fit in any space a stock bulb would fit. | Fans need to have certain space for airflow to be able to sufficiently cool the LED bulbs. Therefore, if you have very tight space behind the dust caps it is not recommended to use the fan cooled bulb. |
Keywords: LED conversion, CONCEPT series, XTREME series, city driving, rural driving, off-road driving, low beam headlight, high beam headlight, projector lamp, fog lights, tight spaces, vehicle lighting, LED headlight, LED fog light, brightness, beam pattern, headlight alignment
Adjust The Mounting Tab:
Check if the LED bulbs are sitting at the right orientation after you install the bulb. If the bulbs are not in the correct orientation, you can adjust the mounting tab to correct the orientation.
For the Concept Series:
1. Observe the angle of the LED diodes and set to the correct angle if needed.
2. Locate the set screw on the LED bulb collar.
3. Use the hex wrench provided to loosen the set screw.
4. Rotate the collar to the required position to achieve correct installation alignment.
5. Tighten the set screw.

For the Xtreme Series:


If you have ever experienced an oncoming driver who’s lights were blinding you or noticed that your lights tend to illuminate the tops of roadside trees instead of the road, there is a good chance that you are dealing with misaligned headlights.
Correct headlight alignment is extremely important for vehicle safety. Driving with misaligned lights is dangerous, and they should be adjusted as soon as possible. Properly aligned headlights not only light up the road, but they also help illuminate road signs and any animals that might jump out onto the road.
Luckily, adjusting your headlights is a pretty easy fix that most people can handle in their driveway or garage. However, newer vehicles that have halogen or high-intensity bulbs should be taken to a professional for proper alignment.
It is fairly simple to check the alignment of your lights. All you need is a flat surface, a wall to project the lights on, a tape measure, a carpenter’s level, a screwdriver, and some tape. Here are step-by-step directions on how to verify your lights are aligned.

Step 1: Prepare the car.
In order to make sure the car is properly leveled when aligning the lights make sure all the tires are properly inflated, the vehicle has at least a half tank of fuel and there is someone sitting in the driver’s seat. This will ensure that the vehicle is leveled and is reflects common driving conditions when the measurements are taken.

Step 2: Park the car.
Find a flat level surface with a wall in front of it and park the vehicle about 10 to 25 feet from the wall or garage door with the lights aimed at the wall. This distance is optimal as it recreates common conditions out on the road. If you have a flat driveway, the garage door should work well, otherwise consider the ground floor of a parking ramp as it is usually flat, dark and has a wall.
Step 3: Level the car.
Push down all four corners of the vehicle up and down a few times to settle the suspension and make sure the shocks are level.

Step 4: Measure the lights.
Use the tape measure to measure from a fixed point on each of the headlamps down to the ground. The measurements should be within a half inch of each other. This will verify the suspension is not sagging on either side, which would throw off the measurements.
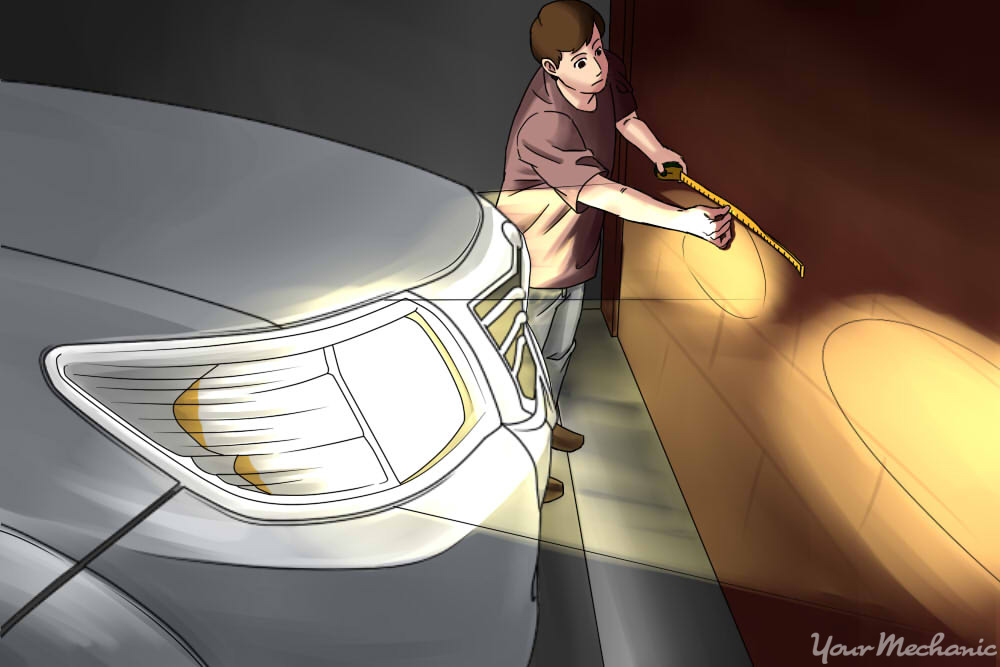
Step 5: Turn on the headlights.
Turn on the lights but do not use the fog lights or high beams. Use the tape to mark both the horizontal and vertical centerlines of the headlight beams.

Step 6: Measure the lines.
The centerlines should not be any higher than 3.5 feet above the ground. Use the carpenter’s level to verify the centerlines from each headlight are even. If the lines are not even, lower the higher mark to the level of the lower one.

Step 7: Back up the car.
The car should now be backed up so it is sitting exactly 25 feet from the wall. This should not be estimated, use the tape measure so the vehicle is exactly 25 feet away.
Now it’s time to make the adjustments to get your lights shining down on the road, where they belong.

Step 1: Find the adjustment screws.
The first thing you need to do is locate the adjustment screws on your vehicle. In many cases, it will be necessary to remove the trim ring from the headlight. Most adjustment screws are located on the top and side of the light housing. They should be clearly marked.
Step 2: Adjust the headlights individually.
If possible, having another person sitting in the driver’s seat that can turn the lights on and off will be a big help. The headlights should be adjusted one at a time. Put a rag or towel over a chair in front of the light you want to block. Covering the light assembly directly can damage the plastic lens – it can get too hot if fully blocked.
Step 3: Adjust the vertical field.
The screw on the top of the light housing should be turned clockwise to raise the lights and counterclockwise will lower the light. The headlight should be adjusted until the top of the most intense part of the light beam shines directly on or just below the center of the tapeline on the wall.

Step 4: Adjust the horizontal field.
The screw on the side of the light housing should now be turned to get the right/left adjustment correct. Adjust the lens so that the most intense part of the beam is to the right of the vertical line.
Step 5: Check manufacturer guidelines.
It is always a good idea to check the manufacturer’s guidelines when adjusting headlights, as there may be very precise specifications that should be followed. This is especially true with the brighter headlights on new vehicles.
Step 6: Test your results.
It’s time to get the vehicle out on the road to make sure the headlights are adjusted properly. This step is important because if you have done the adjustment incorrectly the headlights could be further out of adjustment. Check them on dark road so you can properly judge the adjustment. If they are still not properly adjusted repeat these steps until they correct.
Source of the article: www.yourmechanic.com
by Mark Vallet on January 20, 2016
Keywords: Adjust headlights, Headlight aiming, Headlight adjustment guide, Headlight alignment, Proper headlight adjustment, DIY headlight aiming, Car headlight alignment, Aligning headlights
Let’s say a customer purchases an H16 bulb and finds it doesn’t fit. What is going on, and how come it doesn’t fit?
The problem is that many aftermarket LED manufacturers call the 5202 bulb an H16. However, in Japanese vehicles, the H16 bulb is part of the H9/H11 bulb family. The biggest difference between H8, H9, H11, and H16 bulbs are both the wattage levels they run at and whether or not they have paint on the reflector cap at the top of the glass tube. H16 bulbs are most commonly used in fog lights, whereas H11 bulbs are most commonly used in headlights. Therefore, you’ll see that H11 bulbs look almost identical to H16 bulbs but have higher wattages than H16.
From the photos below, you will see that the H16 is quite different from the 5202.

When you find your car fog light is an H16, if the car is a Japanese vehicle (such as Toyota, Nissan, Lexus, Subaru), the fog light is an H16 (you can also use an H11 to replace it). However, if the car is an American vehicle (such as Chevrolet, GMC, Ford), then the fog light is a 5202 instead of an H16.
Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring you purchase the correct bulb for your vehicle. Always check your vehicle’s manual or consult with a professional before making a purchase.
By being aware of these distinctions, you can avoid the common mistake of purchasing an incorrect bulb for your vehicle.
Let’s say a customer purchases an H16 bulb and finds it doesn’t fit.
What is going on and how come it doesn’t fit?
The problem is all aftermarket LED manufacturers call the 5202 bulb an H16. But in Japanese vehicles, the H16 bulb is part of the H9/H11 bulb family. The biggest difference between H8, H9, H11 and H16 are both the wattage levels that they run at and whether or not they have paint on the reflector cap at the top of the glass tube. H16 are most commonly used in fog lights, whereas the H11 is most commonly used in headlights. Therefore, you’ll see that H11 bulbs look almost identical to H16 bulbs but have higher wattages than H16.
From the below photos, you will find the H16 is quite different with 5202.
So basically, when you find your car fog light is a H16, if the car is Japanese Vehicles (such as Toyota, Nissan, Lexus, Subaru), the fog light is a H16 (you can also use H11 to replace it), but if the car is American Vehicles (such as Chevrolet, GMC, Ford), then the fog light is 5202 instead of a H16.
Keywords: H16 bulb, 5202 bulb, LED bulb compatibility, Japanese vehicles, American vehicles, fog lights, H9/H11 bulb family, aftermarket LED manufacturers, bulb wattage, reflector cap.

To help our customers and partners keep up with the latest information from ARC, please find owner manuals, install guides, and product reference materials below. You may view or download these materials from here.
ARC Tiny Monster Xtreme Series User Manual
ARC Tiny Monster Concept Series User Manual
Visit the ARC Lighting YouTube channel to watch ARC Lighting support and information videos.
For videos on the removal and replacement of your light bulbs and more, we suggest visiting Car Care Kiosk.
By providing these resources, we aim to ensure that you have all the information you need to get the most out of your ARC products.
Keywords: ARC user manuals, ARC reference materials, ARC install guides, ARC product manuals, ARC support documents, ARC Lighting user guides, Download ARC manuals
One of the most common questions we hear every day is what orientation should my LED bulb face? LEDs are “directional” light sources, which means they emit light in a specific direction, unlike halogen bulbs, which emit light in 360°. If not properly oriented, the light will appear to have poor output or beam pattern, and it may cause glare for other drivers. That’s why LED bulbs must be positioned correctly according to the different optical designs of the headlamps.
For single filament bulbs, the diodes (LED chips) should always be in a side-to-side orientation. This means you should have one set of LEDs facing at 3 o’clock and the other set facing at 9 o’clock. This will allow a nice and even 360° light distribution throughout the housing, creating an even beam of light and evenly filling up the housing.

For dual headlight setups that provide low and high beams from one bulb, we use the same side-to-side orientation. Dual beam bulbs have two sets of LED chips on both sides of the bulb. The two chip sets need to be aligned according to the illustration below.

In most cases, all bulbs are initially set to an optimal operating angle, and adjustment is not always required. Check the bulb orientation right away after you install the LED bulbs before any harness is connected. Please check the LED Bulb Adjustment Guide for details on how to adjust the angle of the bulbs.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your LED headlight bulbs provide the best possible performance, with an optimal beam pattern and minimal glare for other drivers.
Keywords: LED headlight bulb orientation, LED headlight alignment, Proper LED bulb orientation, LED bulb positioning, Headlight beam pattern, LED headlight adjustment, Best LED headlight setup
When installing LED headlights in your vehicle, you may encounter issues that indicate the need for a decoder harness. This guide will help you determine if a decoder harness is necessary and explain common problems and solutions associated with LED headlight installations.
Common Issues Requiring a Decoder Harness
When you install LED headlights, you might experience the following problems, which suggest that a decoder harness is needed:
No more errors or flickering. The newly designed decoder harness addresses all these issues! It is designed to handle both CANbus and PWM systems used in the latest vehicles, providing a plug-and-play solution for any LED headlight and fog light conversion. This harness has been tested for compatibility with most Dodge, Chrysler, Jeep, VW, BMW, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, and many other CANbus systems currently in use.
Some CANbus systems monitor the current input of the light bulb they control. When they detect a current larger or smaller than the original bulb’s specification, it causes a problem. The decoder harness can help by accommodating the power demands of the new LED bulb, allowing the system to adjust to the aftermarket product.
Pulse width modulation (PWM) technology is used to reduce the heat output of halogen bulbs, extend their lifespan, and save power. However, LED headlights require a constant current, not the pulsed power supplied by PWM systems. Installing LED headlights in a vehicle with PWM configurations can result in flashing bulbs or bulbs that turn off after a few minutes. The decoder harness includes large capacitors that store power to eliminate the pulse, providing the LED headlights with a constant flow of current.
Keywords: LED headlights, Decoder harness, LED headlight installation,Bulb flashing, Headlight error, CANbus systems, PWM systems, LED headlight problems